Printing technology has come a long way since the invention of the Gutenberg press in the 15th century. From the humble beginnings of manual typesetting to the digital revolution, printing has evolved significantly, shaping the way information is disseminated across the world. In this article, we will delve into the world of modern printing methods, exploring their technologies, applications, and impact on various industries.
1. The Evolution of Printing Technology
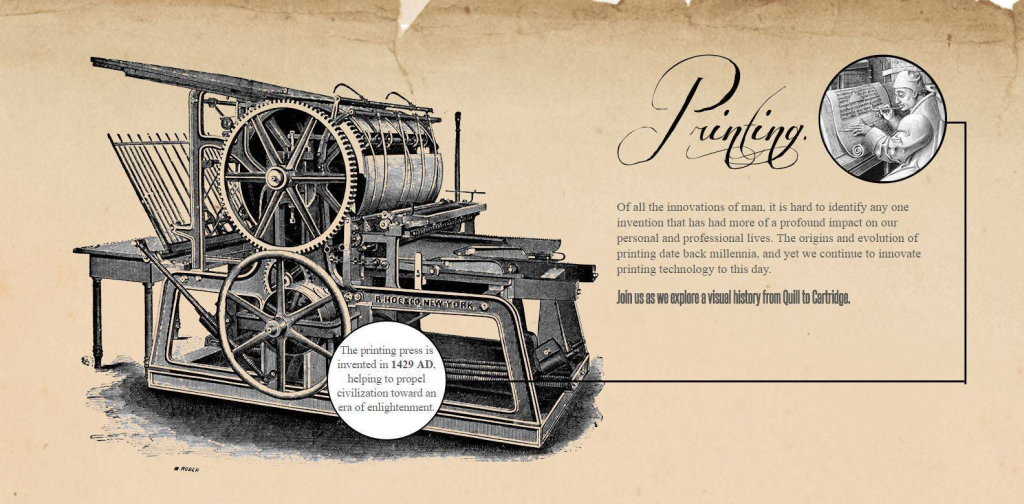
1.1 The Gutenberg Press and the Printing Revolution
The printing revolution initiated by Johannes Gutenberg’s invention of the mechanical movable type press in the 15th century marked a pivotal moment in human history. It drastically reduced the time and cost required to produce books and disseminate knowledge, laying the groundwork for the proliferation of information across continents. The spread of printed materials during the Renaissance period paved the way for the exchange of ideas, leading to cultural, scientific, and societal advancements.
1.2 The Industrial Revolution and the Rise of Offset Printing
The Industrial Revolution brought significant changes to the printing industry. With the introduction of steam-powered presses, printing capacity increased substantially, making books and newspapers more accessible to the general public. The 19th century saw the rise of offset printing, a technique where the image is transferred from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. Offset printing’s high-quality output, cost-effectiveness for large print runs, and compatibility with a wide range of materials made it a popular choice for many applications.
1.3 The Digital Printing Revolution
The late 20th century witnessed the digital printing revolution, which transformed the printing landscape. Digital printing eliminated the need for printing plates, using inkjet or laser technology to create images directly from digital files. It offered advantages such as on-demand printing, variable data capabilities, and minimal setup costs, making it ideal for personalized printing, short runs, and quick turnarounds. The advent of digital printing democratized the printing process, enabling small businesses and individuals to engage in high-quality printing without the need for significant upfront investments.
2. The Main Types of Modern Printing Technology
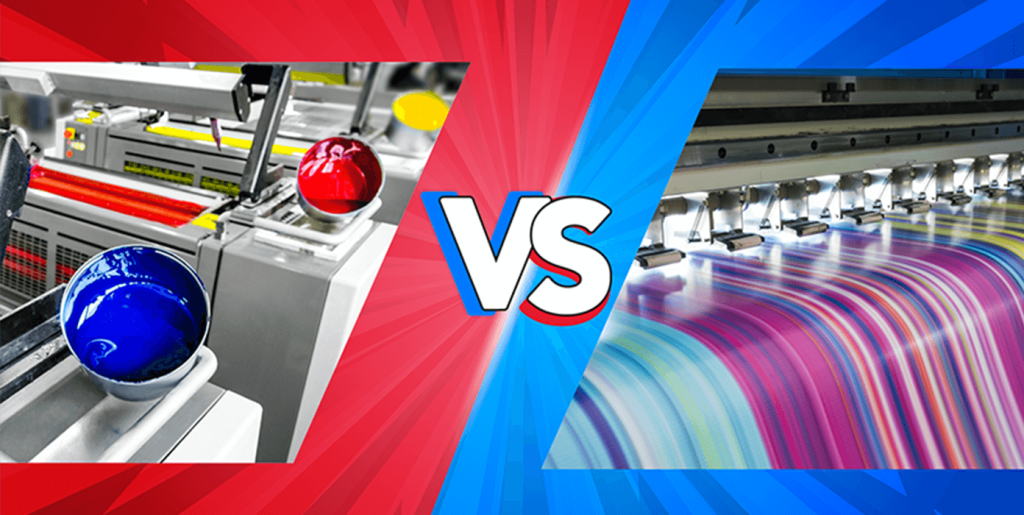
2.1 Offset Printing
Offset printing remains a widely used technology in the publishing industry. Magazines, newspapers, and books are often printed using offset presses due to their ability to handle large print volumes while maintaining consistent and vibrant colors. Additionally, offset printing’s compatibility with various paper types and its exceptional image resolution make it a popular choice for high-quality publications.
2.2 Digital Printing
Digital printing has revolutionized the marketing and advertising sectors by enabling businesses to create personalized promotional materials. From direct mail campaigns with variable data to custom marketing collateral, digital printing has made targeted advertising more effective than ever before. Moreover, digital printing’s capability to produce short print runs economically has reduced waste, making it an environmentally friendly option for businesses looking to minimize their carbon footprint.
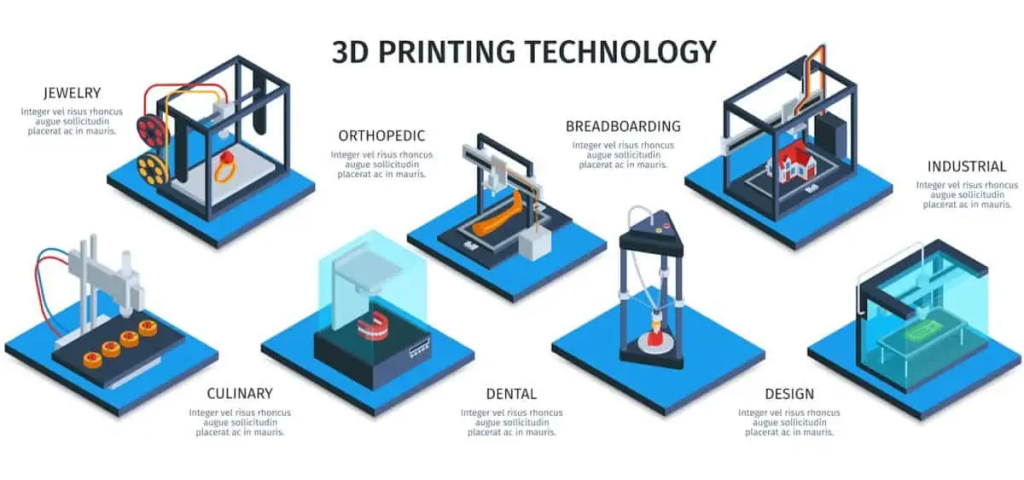
2.3 3D Printing
One of the most exciting and disruptive innovations in recent times is 3D printing. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer. This technology has found applications in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and architecture. In the medical field, 3D printing has facilitated the production of patient-specific implants and prosthetics, revolutionizing the way healthcare professionals approach patient care.
2.4 Flexography
Flexography is a type of relief printing commonly used for packaging materials. It employs flexible relief plates and fast-drying inks, making it suitable for printing on various substrates like plastic, paper, and cardboard. The packaging industry heavily relies on flexography for creating attractive and durable packaging designs for consumer products, food items, and pharmaceuticals.
2.5 Screen Printing
Screen printing continues to be a versatile and popular method for printing on various surfaces. While it has seen significant advancements in automation and image registration, it remains a preferred technique for apparel printing and creating promotional items like t-shirts, tote bags, and posters. Screen printing’s ability to produce vibrant colors on both light and dark fabrics makes it a staple in the fashion and promotional industries.
2.6 Gravure Printing
Gravure printing utilizes engraved cylinders to transfer ink onto the substrate. This method is commonly employed in high-volume printing applications like magazines, catalogs, and packaging due to its consistent and high-quality output. The packaging industry, in particular, benefits from gravure printing’s ability to reproduce intricate designs and provide excellent color consistency.
2.7 Direct-to-Garment (DTG) Printing
Direct-to-Garment printing is a digital printing technique specifically designed for apparel and textile printing. DTG printers can produce highly detailed and vibrant designs directly onto garments, allowing for cost-effective short runs and personalized products. With the rise of e-commerce and print-on-demand services, DTG printing has enabled entrepreneurs and artists to create their clothing lines and custom merchandise with ease.
3. Applications of Modern Printing Technology
3.1 Publishing and Literature
Printing technology remains integral to the publishing industry, producing books, newspapers, and magazines that continue to shape public discourse and entertain readers worldwide. The widespread accessibility of printed material has enabled the sharing of knowledge and cultural heritage across borders, enriching societies and fostering intellectual growth.
3.2 Advertising and Marketing
The printing industry plays a crucial role in advertising and marketing, creating eye-catching banners, brochures, flyers, and promotional materials that drive consumer engagement and brand recognition. Whether it’s a billboard on the side of a highway or a handout at a trade show, printed materials remain an effective and tangible way to reach a target audience.
3.3 Packaging and Labeling
Printing technology is essential for creating attractive and informative product packaging and labels, influencing consumers’ purchasing decisions and ensuring product safety and authenticity. The ability to print product information, barcodes, and branding elements on packaging helps establish a brand’s identity and provides essential details to consumers.
3.4 Healthcare and Biotechnology
The impact of printing technology on the healthcare and biotechnology sectors has been transformative. 3D printing has revolutionized the production of medical devices, prosthetics, and even organs, allowing for personalized healthcare solutions tailored to individual patients. Furthermore, 3D-printed models have significantly improved surgical planning and training for medical professionals.
3.5 Fashion and Textiles
Digital and screen printing have revolutionized the fashion industry by allowing designers to create intricate patterns and custom designs on fabrics, fostering creativity and individuality in clothing and home textiles. Custom apparel, such as t-shirts, hoodies, and sportswear, has become increasingly popular due to advancements in printing technology that offer vibrant, long-lasting prints on various textiles.
3.6 Electronics and Technology
Printing technology plays a role in the manufacturing of electronic components, including circuit boards and conductive inks, driving advancements in consumer electronics and wearable tech. Printed electronics have led to the development of flexible displays, smart textiles, and innovative devices that enhance the functionality and convenience of modern gadgets.
3.7 Architecture and Construction
3D printing has also made significant strides in the architecture and construction industries. The ability to 3D print building components, such as walls and structural elements, has the potential to revolutionize construction processes, making them more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable. Additionally, 3D printing has been explored as a means to construct housing in remote and underprivileged areas, offering an innovative solution to global housing challenges.
4. The Future of Printing Technology

4.1 Nanotechnology and Conductive Inks
Advancements in nanotechnology have led to the development of conductive inks, expanding the potential of printed electronics, including flexible displays, sensors, and wearable devices. As nanotechnology continues to evolve, we can expect even more compact, energy-efficient, and multifunctional printed electronics to emerge, enabling a new era of smart and interconnected devices.
4.2 Sustainable Printing
As environmental concerns grow, the printing industry is embracing sustainable practices, such as eco-friendly inks, recycled materials, and energy-efficient printing processes. Sustainability has become a key focus for businesses, and the printing industry is no exception. Manufacturers and consumers alike are seeking ways to reduce their ecological footprint, and sustainable printing practices offer a viable solution to address these concerns.
4.3 Bioprinting and Organ Manufacturing
Bioprinting holds the promise of revolutionizing healthcare by enabling the creation of human tissues and organs, addressing the organ transplant shortage and advancing regenerative medicine. Scientists and researchers are continually exploring ways to use bioprinting to create complex tissues and organs with functional capabilities, opening up new possibilities in personalized medicine and organ transplantation.
4.4 Artificial Intelligence and Automation
The integration of artificial intelligence and automation in printing processes streamlines production, reduces errors, and enhances efficiency, propelling the industry towards a more digitized and connected future. AI-driven printing technologies can optimize print layouts, color management, and quality control, ensuring consistent and high-quality results. Automation also facilitates faster production times, enabling printers to meet the increasing demands of the market.
4.5 Virtual and Augmented Reality in Printing
With the rise of virtual and augmented reality technologies, printing has found new dimensions of interaction and engagement. Brands and marketers are exploring ways to integrate printed materials with immersive experiences. Interactive printed materials, such as QR codes and augmented reality elements, bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds, creating novel and engaging ways to deliver content and information.
4.6 Cross-Media Integration
Modern printing technology is increasingly integrated with other media channels, such as social media, websites, and email marketing. Cross-media campaigns allow businesses to deliver a consistent message across various platforms, maximizing their reach and impact. By combining print and digital elements, businesses can create powerful and memorable customer experiences.
4.7 Education and Learning Applications
Printing technology plays a vital role in education, from textbooks and workbooks to interactive learning materials. The integration of 3D printing in educational settings fosters hands-on learning experiences and encourages creativity in students. Additionally, personalized learning materials, tailored to individual student needs, can be efficiently produced using digital printing methods.
Conclusion
Printing technology has undergone a remarkable transformation, from the revolutionary Gutenberg press to the current era of digital printing and 3D printing. As technology continues to advance, the printing industry will play an increasingly significant role in various sectors, driving innovation, creativity, and sustainability. Embracing the potentials of new printing technologies will shape a future where information, art, and functionality intertwine seamlessly. From personalized advertising to life-saving medical advancements, modern printing methods continue to shape the world we live in, making a lasting impact on our daily lives and paving the way for a more interconnected and efficient global society.
With the relentless pursuit of innovation, the printing industry is bound to bring even more exciting possibilities in the years to come, transforming industries, enriching lives, and pushing the boundaries of human ingenuity. The integration of artificial intelligence, nanotechnology, and sustainable practices will redefine the printing landscape, making it more responsive, eco-friendly, and accessible to a broader range of users. As we embrace these advancements, the future of printing technology looks bright, promising a world where information and creativity know no bounds.